Heap Sort Implementation
코드 구현 원칙
- 수도코드보고 구현
- 실패시, 코드보고 코멘트 달고 작성해보기
- 재귀로 구현 완성
- iterative version 구현하기
Pseudo Code
- siftdown 구현
- left child, right child
- largest
- swap
- recursion
- heapify 구현
- 전체 노드가 아닌 len//2 -1 의 index부터 시작해서 sort
- heapsort 구현
- heapify 함수로 max heap 구조를 만든 후 root와 end 노드를 swap하고 siftdown 수행
- swap, siftdown 수행후 end를 하나씩 줄여나간다.
- heapify 함수로 max heap 구조를 만든 후 root와 end 노드를 swap하고 siftdown 수행
재귀호출 구현
def heapsort(a):
def siftdown(a, i, size):
l = 2*i + 1
r = 2*i + 2
largest = i
if l <= size-1 and a[l] > a[i]:
largest = l
if r <= size-1 and a[r] > a[largest]: # 자식노드 2개중 큰 것을 largest 변수에 넣어야 하기 때문에, r에서는 largest와 r을 비교
largest = r
if largest != i: # largest가 i와 다르다면, 즉, largest가 변경되었다면, swap을 해주고 siftdown
# SWAP
a[i], a[largest] = a[largest], a[i]
siftdown(a, largest, size)
def heapify(a, size):
p = (size//2)-1
while p>=0:
siftdown(a, p, size)
p -= 1
size = len(a)
heapify(a, size) # MAX HEAP
end = size-1
while(end > 0):
# root와 end를 swap 해준 후
# root를 siftdown 해주면 정렬이 된다.
# (swap된 노드(root에서 swap했으므로 현재는 end노드)는 siftdown에서 배제된 상태로 siftdown 진행된다.)
# (root는 heapify된 후 이므로 최고 혹은 최소이기 때문에)
a[0], a[end] = a[end], a[0]
siftdown(a, 0, end) # root node 부터 siftdown을 진행
end -= 1
Compare with Merge Sort
- summary:
- Heap:
- Unstable Sort
- in-place: memory efficienty
- Merge:
- Stable Sort
- \(O(n)\) extra space is required.
- Heap:
Stability in Sorting Algorithms
- The stability of a sorting algorithm is concerned with how the algorithm treats equal (or repeated) elements.
- Stable sorting algorithms preserve the relative order of equal elements, while unstable sorting algorithms don’t.
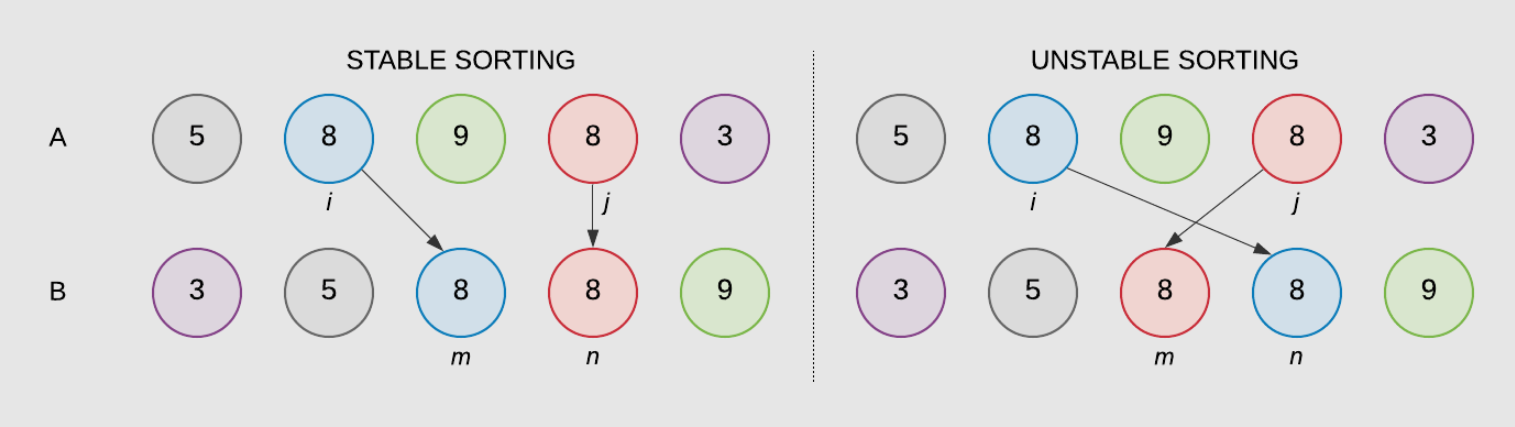
When Stability Matters
- Distinguishing Between Equal Elements
- If the sort key is the (entire) element itself, equal elements are indistinguishable, such as integers or strings.
- Stable Sorting Is Important, Sometimes
- We don’t always need stable sorting. Stability is not a concern if:
- equal elements are indistinguishable, or
- all the elements in the collection are distinct
- We don’t always need stable sorting. Stability is not a concern if:
- When equal elements are distinguishable, stability is imperative.
- For instance, if the collection already has some order, then sorting on another key must preserve that order.
Stable and Unstable Sorting Algorithms
- Stable: Merge Sort, Timsort, Counting Sort, Insertion Sort, and Bubble Sort.
- Unstable: Quicksort, Heapsort and Selection Sort.
Iterative Heap Sort (TODO)
Appendix
Reference
힙 정렬 알고리즘 Heap Sort (part 1/2): https://youtu.be/WDm8a9GvQyU
Heap sort vs Merge sort || Comparision between heap sort and merge sort: https://youtu.be/5DYZEcSj2dE
Stability in Sortin Algorithm: https://www.baeldung.com/cs/stable-sorting-algorithms Stability in Sortin Algorithm: https://blog.naver.com/zephyehu/150013176075 Stability in Sortin Algorithm: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stability-in-sorting-algorithms/

Leave a comment